Promise
비동기로 처리하기 위한 방법 중 하나.
다음과 같이 사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
//Promise 선언
var _promise = function (param) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
window.setTimeout(function () {
if (param) {
resolve("해결 완료");
} else {
reject(Error("실패!!"));
}
}, 3000);
});
};
//Promise 실행
_promise(true).then(
function (text) {
// 성공시
console.log(text);
},
function (error) {
// 실패시
console.error(error);
}
);
위에서는 .then()에 함수를 두개 넣어서 각각 성공, 실패시에 대응하고 있다. 하지만 에러를 잡아낼때는 다음과 같이 .catch()가 더 자주쓰인다. 체이닝 중간에 넣을 수 있기때문이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
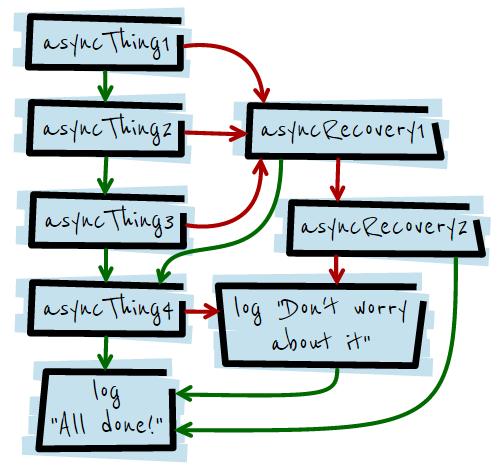
asyncThing1()
.then(function () {
return asyncThing2();
})
.then(function () {
return asyncThing3();
})
.catch(function (err) {
return asyncRecovery1();
})
.then(
function () {
return asyncThing4();
},
function (err) {
return asyncRecovery2();
}
)
.catch(function (err) {
console.log("Don't worry about it");
})
.then(function () {
console.log("All done!");
});
위 로직을 그림으로 표현하면 다음과 같다
Promise.all
여러 프로미스를 모두 완료될때까지 기다리는 방법이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
var promise1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
window.setTimeout(function () {
console.log("첫번째 Promise 완료");
resolve("11111");
}, Math.random() * 20000 + 1000);
});
var promise2 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
window.setTimeout(function () {
console.log("두번째 Promise 완료");
resolve("222222");
}, Math.random() * 10000 + 1000);
});
Promise.all([promise1, promise2]).then(function (values) {
// values에는 배열 형태로 resolved value가 들어옴
console.log("모두 완료됨", values);
});
바로 new Promise 생성하기
Promise.all 예시처럼 return 하지 않고 바로 new Promise를 생성하면, 파라미터로 넘겨준 익명함수는 바로 실행된다. 따라서 다음과 같이 사용가능하다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
if (+new Date() % 2 === 0) {
resolve("Stuff worked!");
} else {
reject(Error("It broke"));
}
})
.then(alert)
.catch(alert);
만약 Promise.all 예시에서 return으로 Promise 객체를 반환했다면 코드를 아래와 같이 변경해야한다.
1
2
3
Promise.all([promise1(), promise2()]).then(function (values) {
console.log("모두 완료됨", values);
});
Async, await
Promise와 같이 비동기를 처리하는 방법이다. 하지만 좀 더 간단하고 이해하기 쉽다.
- Promise로 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
function makeRequest() {
return getData()
.then((data) => {
if (data && data.needMoreRequest) {
return makeMoreRequest(data)
.then((moreData) => {
console.log(moreData);
return moreData;
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log("Error while makeMoreRequest", error);
});
} else {
console.log(data);
return data;
}
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log("Error while getData", error);
});
}
const makeRequest = () => {
return promise1().then((value1) => {
// do something
return promise2(value1).then((value2) => {
// do something
return promise3(value1, value2);
});
});
};
- async/await로 구현
- 에러처리는 try/catch로 할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
async function makeRequest() {
try {
const data = await getData();
if (data && data.needMoreRequest) {
const moreData = await makeMoreRequest(data);
console.log(moreData);
return moreData;
} else {
console.log(data);
return data;
}
} catch (error) {
console.log("Error while getData", error);
}
}
const makeRequest = async () => {
const value1 = await promise1();
const value2 = await promise2(value1);
return promise3(value1, value2);
};
출처
https://programmingsummaries.tistory.com/325
https://github.com/JaeYeopHan/Interview_Question_for_Beginner/tree/master/JavaScript#promise
